Abstract:
Smart Factory Automation represents a paradigm shift in the manufacturing industry. It integrates advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and computer vision to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve quality. Here we explore the transformative power of smart factory automation, providing an in-depth analysis of its benefits and its impact on the manufacturing landscape.
Introduction
The concept of the Smart Factory Automation has ushered in a new era of manufacturing. Unlike traditional factories, Smart Factories leverage cutting-edge technologies to optimize operations, streamline production, and achieve unparalleled levels of efficiency, cost reduction, and quality improvement. This whitepaper delves into the multifaceted benefits of Smart Factory Automation.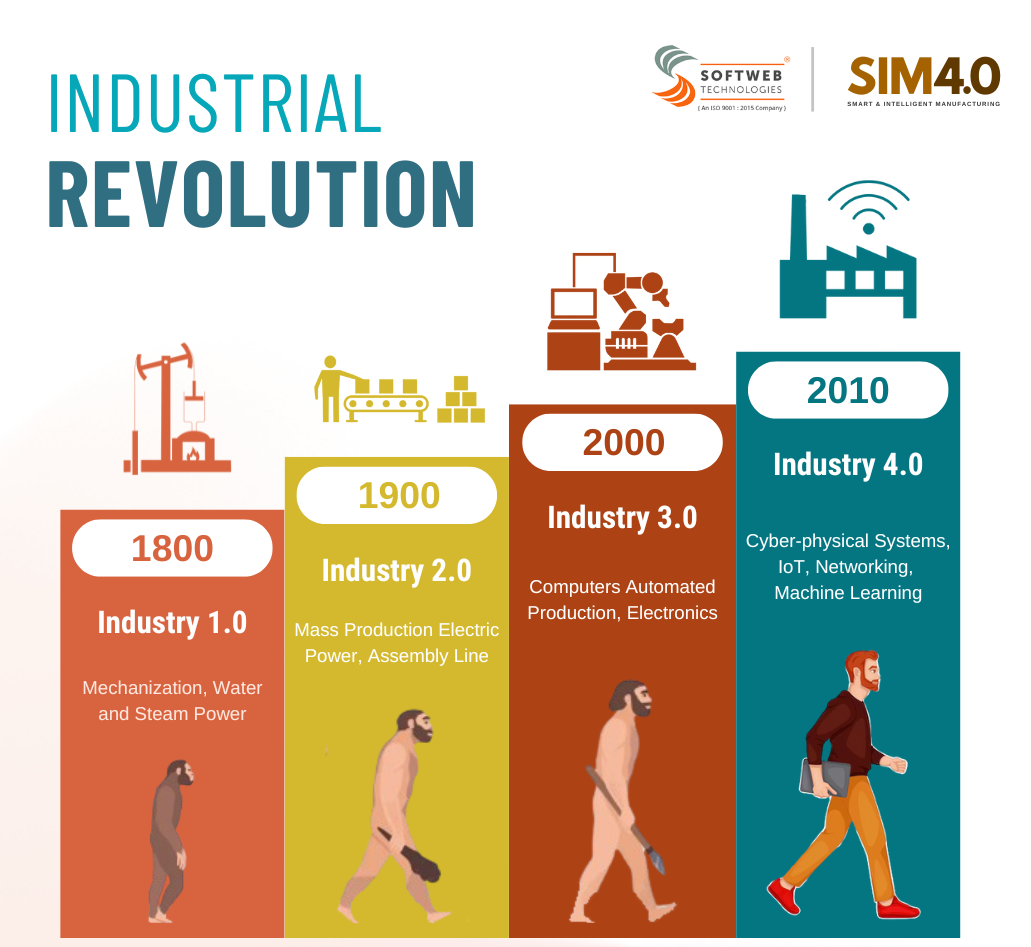
Wondering what is Industry 4.0 or Smart factory automation? Click here to know more.
1. Enhanced Efficiency
One of the most compelling advantages of Smart Factory Automation is the significant enhancement in efficiency:
1.1. Real-time Data Analytics: Smart factories collect and process data in real-time, enabling manufacturers to monitor every aspect of the production process. This data-driven approach allows for swift decision-making, predictive maintenance, and process optimization.
Predictive maintenance is a proactive maintenance strategy that uses data and advanced analytics to predict when a piece of equipment or machinery is likely to fail so that maintenance can be performed just in time to prevent the failure. This approach is in contrast to traditional or reactive maintenance, where equipment is serviced or repaired only after it breaks down.
1.2. Reduced Downtime: Automation minimizes downtime, as machines can operate 24/7 without human intervention. Predictive maintenance schedules based on real-time data further reduce unplanned interruptions.
1.3. Process Optimization: Machine learning algorithms continuously improve processes, adjusting parameters to ensure peak performance, and reducing wastage. These optimizations extend to supply chain management and inventory control.
Softweb Technologies’ SIM 4.0 helps major manufacturing plants to attain smart factory automation in their premises.
2. Cost Reduction
Smart Factory Automation also offers substantial cost-saving benefits:
2.1. Energy Efficiency: Automation systems can optimize energy consumption, leading to substantial savings. For example, lighting, heating, and cooling can be controlled based on occupancy, while machines can operate at peak efficiency.
2.2. Reduced Material Wastage: Automation systems optimize material usage, leading to reduced waste. The precision and consistency of machines contribute to this significant cost reduction.
3. Improved Quality
The application of automation in smart factories translates to superior product quality:
3.1. Consistency and Precision: Automated processes eliminate the variability inherent in manual operations. This consistency results in products of higher quality, adhering to precise specifications.
3.2. Real-time Quality Control: Advanced sensors and vision systems enable real-time quality control, identifying defects and deviations from quality standards. Defective items can be automatically removed from the production line.
3.3. Traceability: Smart factories can trace products through the entire production process, from raw materials to finished goods. This traceability allows for rapid identification and mitigation of quality issues.
4. Supply Chain Benefits
Smart Factory Automation extends its advantages beyond the factory floor, impacting the entire supply chain:
4.1. Demand Forecasting: Accurate data collection and analysis enable better demand forecasting, reducing overstock and understock situations, leading to improved customer satisfaction and reduced carrying costs.
4.2. Reduced Lead Times: Automation streamlines production and logistics, significantly reducing lead times and enabling quicker response to market demands.
4.3. Supplier Integration: Smart factories can integrate seamlessly with suppliers, creating a connected ecosystem that facilitates just-in-time deliveries and minimizes inventory holding costs.
5. Human-Machine Collaboration
It is essential to acknowledge that smart factory automation does not eliminate the human element. Instead, it enhances the roles of employees:
5.1. Skilled Workforce: Automation requires skilled personnel to design, program, and maintain the systems. This fosters opportunities for upskilling the workforce.
5.2. Safer Work Environment: Automation often handles hazardous tasks, improving workplace safety and reducing workplace accidents.
6. Security and Data Privacy
The adoption of smart factory automation brings new challenges related to security and data privacy:
6.1. Cybersecurity: With increased connectivity, smart factories become targets for cyberattacks. Manufacturers must invest in robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard their data and operations.
6.2. Data Privacy: The vast amount of data collected by smart factories necessitates strict data privacy policies and compliance with regulations like GDPR to protect sensitive information.
7. Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of Smart Factory Automation are undeniable, there are challenges to overcome:
7.1. Initial Investment: Implementing automation systems requires a significant upfront investment in technology and workforce training.
7.2. Workforce Transition: Transitioning to automation may lead to job displacement, necessitating careful planning for reskilling or redeployment of workers.
7.3. Maintenance and Upkeep: Automation systems require regular maintenance and updates to ensure they continue to operate at peak performance.
Softweb Technologies’ SIM 4.0 as Smart Factory Automation represents a transformative shift in manufacturing, offering unparalleled benefits in efficiency, cost reduction, and quality improvement. It empowers manufacturers to remain competitive in an ever-evolving market landscape while also positively impacting the workforce and supply chain.
The challenges it presents, such as initial investments and workforce transition, can be effectively managed with thoughtful planning. It has been found out, the investments made by organizations for transitioning to Smart Factory Automation, has been recovered within few years of production. As technology continues to advance, Smart Factory Automation will play an even more crucial role in shaping the future of manufacturing. Embracing this paradigm shift is essential for businesses looking to thrive and excel in the 21st-century industrial landscape.

