Smart farming & Precision Agriculture are reshaping modern agriculture through technology-driven strategies like IoT, AI, and data analytics. These approaches help optimise crop management, enhance resource efficiency, and minimise environmental impact. From precision input application to real-time monitoring, these innovations are crucial for addressing future challenges in farming and ensuring sustainable food production.
These data once analyzed with Farm and Plantation ERP, can help farmers take data driven decisions for sustainable farming
What Is Smart Farming?
Smart farming refers to the integration of advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and robotics to enhance agricultural processes. It aims to make farming more efficient, sustainable, and data-driven. By utilising real-time data and automation, smart farming helps farmers monitor crops, livestock, and environmental conditions, leading to improved decision-making. This approach also reduces resource waste and enhances productivity, contributing to sustainable agriculture.
What Are The Technologies Used In Smart Farming?
Smart farming employs a range of technologies, including:
-
IoT : These sensors collect data on soil moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels to optimise irrigation and fertilization.
-
Drones and satellites: These used for aerial monitoring, providing insights into crop health and growth patterns.
-
Robotics: Autonomous machines perform tasks like planting, weeding, and harvesting with precision.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI analyzes collected data to predict weather patterns, pest infestations, and crop diseases.
What Is Precision Agriculture?
Precision agriculture is a farming technique that involves using data and technology to optimize the application of inputs such as water, fertilizer, and pesticides in specific areas. It focuses on site-specific crop management, aiming to increase productivity and reduce resource waste.
How Is Precision Agriculture Different From Traditional Farming?
Precision agriculture differs from traditional farming by focusing on precise, data-driven actions. While traditional farming treats an entire field uniformly, precision agriculture tailors inputs to specific field zones, enhancing efficiency and sustainability.
Smart Farming & Precision Agriculture: Technologies & Solutions
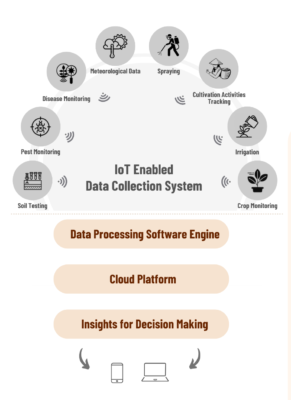
Advanced techniques like soil testing, pest monitoring, irrigation management, and crop monitoring are transforming agriculture, and how solutions like GIS-based systems, mobile apps, and sensor integration are enhancing field-level data tracking.
Soil Testing: The Foundation of Smart Farming
Soil quality is crucial for determining crop health and yield. Traditional methods of soil testing were time-consuming, but smart farming leverages sensors to collect data on NPKS levels (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium, Sulfur), pH levels, and moisture content.
Pest and Disease Monitoring
One of the major challenges in farming is controlling pests and diseases, which can severely impact crop yield. Precision agriculture uses computer vision and image processing technologies to analyze crops for signs of pests and diseases.
Meteorological Data & Irrigation Management
Smart farming incorporates weather station integration to provide real-time meteorological data, helping farmers make informed decisions regarding irrigation schedules and crop management. By predicting rainfall, temperature fluctuations, and humidity, farmers can ensure that their crops receive adequate water without overuse, thus promoting both efficiency and sustainability.
Crop Monitoring and Cultivation Activity Tracking
Tracking the entire cultivation process—from planting to harvest—is now possible through GIS-based solutions and mobile apps. These technologies allow farmers to monitor growth stages, track field activities, and ensure that operations run smoothly.
Smarter Decisions with Smart Farming & Precision Agriculture
Soil and Water Sensors
Soil sensors are integral to precision agriculture, capturing real-time data on key soil parameters, such as moisture levels, temperature, and nutrient content. Farmers can use this data to adjust watering and fertilization practices in real time, ensuring that crops receive just the right amount of nutrients and water.
Similarly, water level sensors in irrigation systems provide critical information on water availability. By automating irrigation schedules based on soil moisture readings, farmers can reduce water waste, lower costs, and prevent overwatering.
Disease and Pest Analysis with Computer Vision
Computer vision, through image processing, identifies plant diseases and pest infestations at their earliest stages. Cameras or drones take images of crops, which are then analyzed by algorithms to detect visual anomalies. This early detection allows farmers to intervene quickly, protecting crop health and minimizing yield loss.
Drone-Based Spraying and Satellite Image Processing
Drones are becoming a powerful tool for precision agriculture, especially in spraying applications. Unlike traditional methods, which involve uniform pesticide distribution, drone-based spraying allows farmers to apply pesticides only where needed. This reduces the overall pesticide use and minimizes the risk of contaminating non-target areas.
Data Analytics Engine and Dashboard for Real-Time Insights
All these technologies generate massive amounts of data that can be difficult to interpret without the right tools. A data analytics engine processes field data from sensors, weather stations, and satellite images to deliver actionable insights through an intuitive dashboard. This real-time information helps farmers track field activities, monitor soil health, and predict crop yields, empowering them to make informed decisions that enhance efficiency and sustainability.
Mobile Apps and GIS-Based Solutions for Field Level Data Capturing
Mobile apps have revolutionised precision agriculture by putting critical data at farmers’ fingertips. GIS-based mobile apps help track cultivation activities such as seeding, ploughing, and spraying, providing real-time updates on farm operations. With geo-tagging, farmers can track the specific location of tasks and assess crop health across different sections of the field.
Sustainable Business Practices in Smart Farming
Precision agriculture and smart farming technologies are key to promoting sustainable farming practices. By optimising the use of water, fertilisers, and pesticides, farmers can significantly reduce their environmental footprint while maintaining profitability. Smart farming also encourages responsible land management, soil conservation, and biodiversity protection.

